What is Tumor Microenvironment (TME)?
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a constantly changing framework intricately linked with cancer cells, largely influenced by their presence. Distinctive traits of the TME include irregular blood vessels, hypoxia, acidic pH levels outside cells, modifications in the extracellular matrix, and stromal components like cancer-associated fibroblasts, macrophages, and immune cells (Marie-France Penet, Samata Kakkad & Jesus Pacheco-Torres, et.al, 2021)
Cytokines and the Tumor Microenvironment
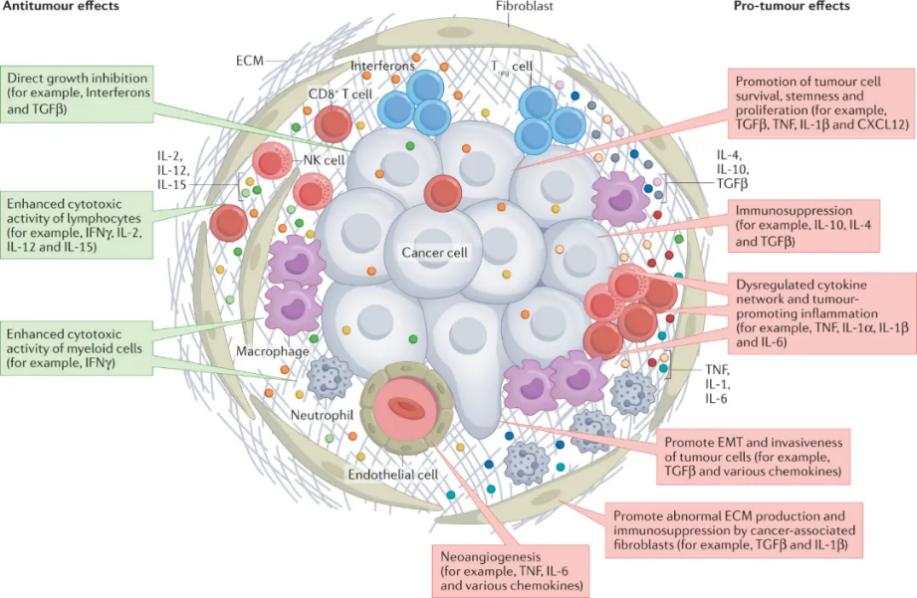
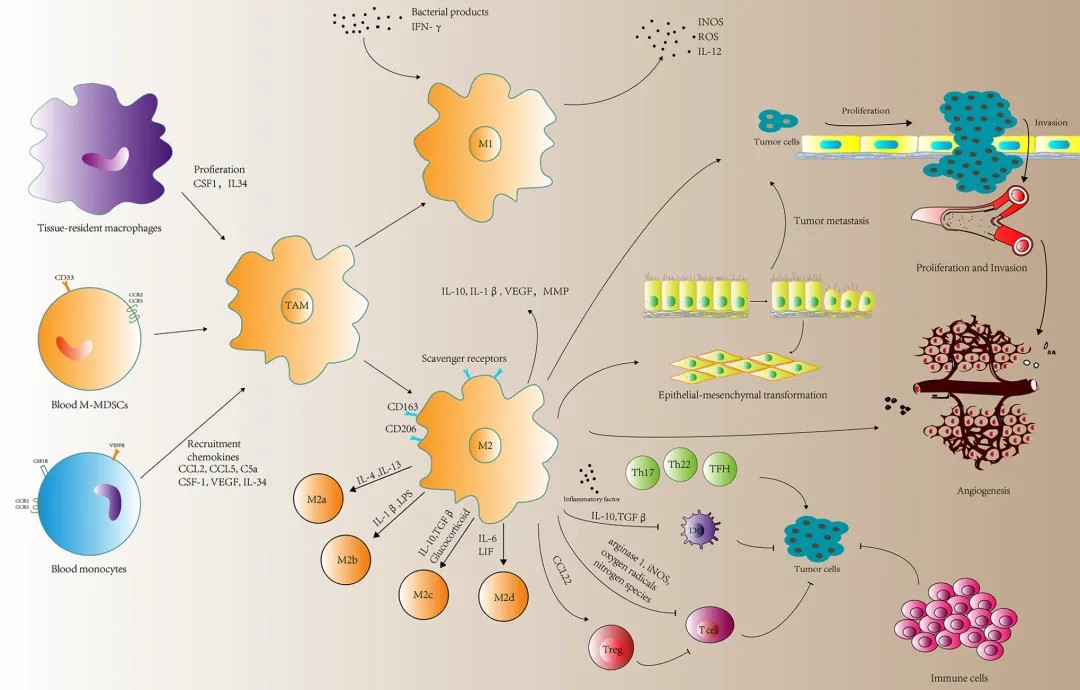
Cytokines play a crucial role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) by acting as signaling molecules that mediate interactions between cancer cells and the surrounding stromal components. One of the three major characteristics of the TME is the presence of chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation promotes cancer cell proliferation, matrix degradation and remodeling, angiogenesis, and immune suppression, thereby facilitating tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. Inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 can activate M2-type macrophages, participate in the formation of Th2 cells, and promote the occurrence and development of tumors.
For example:
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-1β, among others, are capable of promoting the survival and proliferation of tumor cells.
- TNF and IL-6, among others, can disrupt cytokine regulation and promote tumor inflammation.
Cytokines’ clinical significance
|
Clinical application
|
Indicators
|
Significance
|
|
Auxiliary Diagnosis of the Type of Infectious Disease
|
Elevated levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 in non-tumor patients
|
Suggests a possible bacterial infection
|
|
IFN-γ > 100 pg/ml in non-tumor patients.
|
Suggests the possibility of a mycobacterial infection
|
|
IFN-γ ≤ 100 pg/ml in non-tumor patients, along with elevated levels of IL-1β, IL-6, etc.
|
Suggests the possibility of a viral infection
|
|
Evaluation of Early Stage Infection, Severity of Infection, Inflammation, Sepsis, and Efficacy of Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Therapy
|
Elevated levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and IL-17 in infection and sepsis patients, often accompanied by decreased IL-2 levels.
|
Indicates the severity of infection or sepsis, with IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and IL-17 levels typically elevated in such conditions.
|
|
Elevated levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and IL-12P70 in critically ill patients.
|
Indicates that the condition is critical, with significant infection present. In such cases, levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and IL-12P70 are often elevated.
|
|
To assist in the diagnosis of other diseases
|
IL-10 levels > 10% and elevated IFN-γ in patients
|
Suggests hemophagocytic syndrome; EBV infection needs to be ruled out. In pediatric EB viral infection patients, IFN-γ > 100 p/ml and IL-10 > 60 pg/ml, and IFN-γ>IL-6.
|
|
Elevated levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-17
|
Indicates the possibility of allergic diseases.
|
|
Applications in reproduction area
|
For patients with infertility or recurrent miscarriages, elevated levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-17, along with decreased levels of IL-10
|
Suggesting that the etiology of the patient's condition may be attributed to immune dysfunction, if during both passive and active treatments the levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, IFN-α, and IL-17 gradually decrease while the IL-10 level gradually increases, it indicates that the treatment is effective for the patient.
|
Poclight Bio has developed the fifth-generation dry chemical luminescence platform based on the "Chemiluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (CRET)" technology. It not only possesses the advantages of traditional chemiluminescence technology such as high precision, high sensitivity, and wide signal range but also utilizes the characteristics of graphene oxide, eliminating the need for magnetic beads and thus removing the separation and cleaning steps. The entire reaction only requires three steps: sample addition, incubation, and detection, without the need for multiple washing and separation steps, resulting in a simpler structure, shorter time, and lower failure rate. It achieves homogeneous luminescence without complex liquid paths.
Thirteen cytokines have been studied, and each factor can be matched as needed to solve various clinical treatment problems, such as distinguishing between viral and bacterial infections and real-time monitoring of treatment efficacy.
Poclight’s Reagents
|
1
|
IL-1β
|
|
2
|
IL-2
|
|
3
|
IL-2 Receptor
|
|
4
|
IL-4
|
|
5
|
IL-5
|
|
6
|
IL-6
|
|
7
|
IL-8
|
|
8
|
IL-10
|
|
9
|
IL-12p70
|
|
10
|
IL-17A
|
|
11
|
IFN-α
|
|
12
|
IFN-γ
|
|
13
|
TNF-α
|
C5000 Hot Sale Chemiluminescence Immunoassay Analyzer
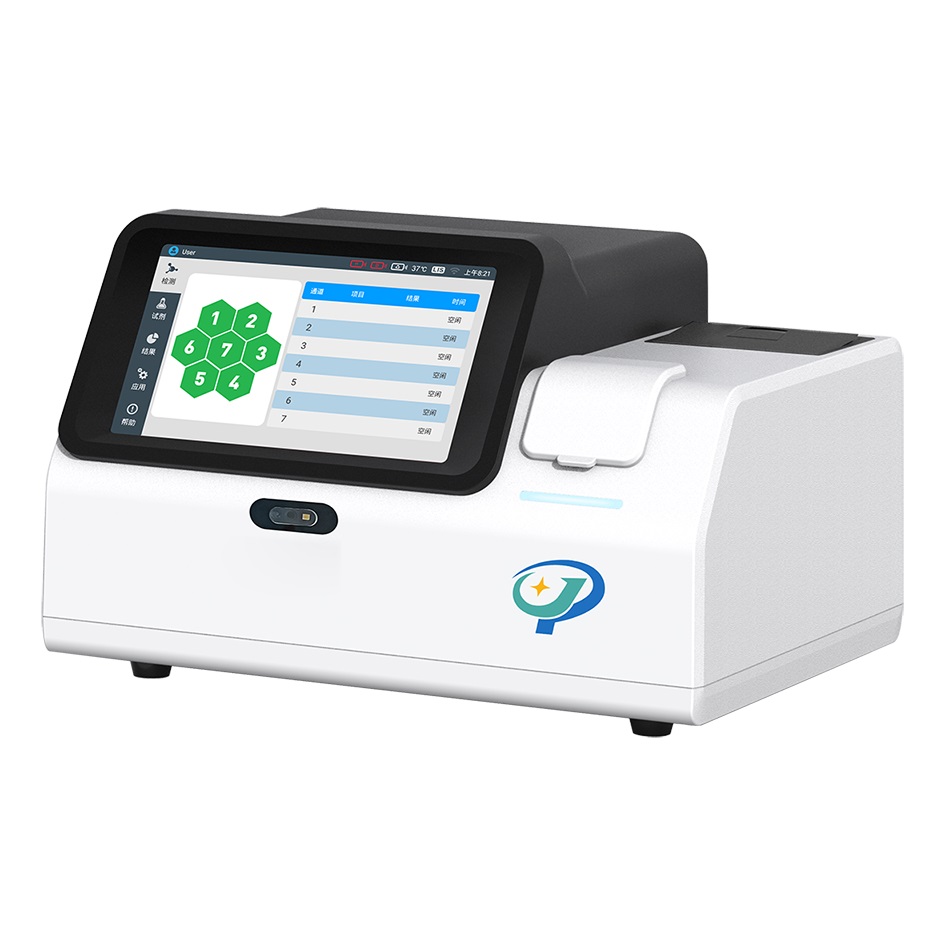

New era of POCT CLIA analyzer
Features:
Time to results: 3~15 mins
Loading capacity: 7 tests at one time
Storage: Lyophilized reagents room temperature
Sample types: Whole blood, Serum, Plasma, etc.
Principle: CERT Homogeneous CLIA
Dimensions: 325*231*213 mm
Communication: LIS/HIS/5G transmission
Package: single package
Accurate:CV ≤3
Reference:
Marie-France Penet, Samata Kakkad, Jesus Pacheco-Torres, Santosh Bharti, Balaji Krishnamachary, Zaver M. Bhujwalla, Chapter 53 - Molecular and Functional Imaging and Theranostics of the Tumor Microenvironment, Editor(s): Brian D. Ross, Sanjiv Sam Gambhir, Molecular Imaging (Second Edition),Academic Press,2021,Pages 1007-1029, ISBN 9780128163863, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816386-3.00069-7.

 English
English français
français русский
русский español
español português
português العربية
العربية 日本語
日本語 Türkçe
Türkçe हिंदी
हिंदी Indonesia
Indonesia 








 IPv6 network supported |
IPv6 network supported | 